رَبِّ زِدْنِي عِلْماً
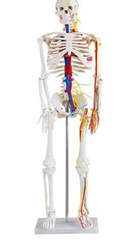
Skeleton with Nerves and Blood Vessels
Bone And Joint
₹82.00₹22.00
The human body is a complex and intricate system, and at its core lies a structure that provides both support and protection: the skeleton. The skeleton is made up of 206 bones in the adult human, which serve as the framework of the body, allowing us to stand upright, move, and protect vital organs. However, this bony structure does not operate in isolation; it is thoroughly integrated with nerves and blood vessels that play crucial roles in maintaining health and function. The skeletal system can be broadly divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton, which comprises the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage, and the appendicular skeleton, which includes the bones of the limbs and the pelvic girdle. Each bone has a unique shape and function, from the flat bones of the skull that protect the brain to the long bones of the limbs that facilitate movement. Within and around these bones, a fascinating network of nerves and blood vessels thrives, enabling the skeleton to communicate with the rest of the body. The periosteum, a dense layer of connective tissue, covers the outer surface of bones and is rich in blood vessels and nerve fibers. This layer not only nourishes the bone but also provides a conduit for nerves; it is where sensory information about pain, pressure, and vibrations is relayed. Such sensations are essential, as they help protect the bones from injury and aid in their repair. Blood vessels, particularly the arteries and veins, play a pivotal role in bone health. The bone itself is a living tissue that requires a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients. Blood vessels penetrate the bone through tiny openings known as foramina, creating an intricate system that supports the growth and maintenance of bone cells. Within the bone, organized cavities house bone marrow, where blood cells are produced. This multifaceted relationship between blood vessels and bones ensures that the skeleton remains strong and capable of performing its myriad functions. Nerves also play a vital role in coordinating movement and maintaining balance. The central nervous system communicates with skeletal muscles via motor neurons, causing contraction and relaxation as needed. This connection is particularly evident in reflex actions, where rapid responses to stimuli involve the skeletal system working in tandem with nerves, highlighting the importance of this integration for protection and function. Moreover, disturbances in the relationship between bones, blood vessels, and nerves can lead to various health issues. Conditions such as osteoporosis weaken bones, making them fragile and susceptible to fractures. Neuropathy, on the other hand, can diminish the communication between nerves and muscles, leading to challenges in coordination and balance. Thus, understanding the synergy between the skeleton, nerves, and blood vessels is essential not only for medical professionals but for anyone interested in maintaining a healthy body. Awareness of how these systems interact can inform practices ranging from preventative care to rehabilitation following injuries. In summary, the skeleton serves as the vital foundation of the human body, intricately connected with nerves and blood vessels that together ensure our mobility and overall well-being. This relationship underscores the complexity of the human body and the importance of viewing it as an interconnected system, where every element is crucial for optimal performance and health.
Training
Providing essential healthcare training and simulation solutions.
COntacts
Support
info@medisureinternational.com
Address : 292, 7th main road Vyalikaval HBCS layout , Bangalore - 560045
+91 9972123423
© Medisure. All Rights Are Reserved
Crafted by Influence Kashmir
