رَبِّ زِدْنِي عِلْماً
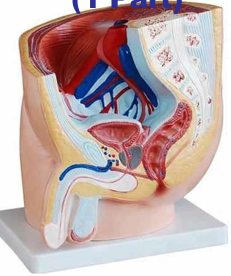
Human Male Pelvis Section (1 Part)
Embryology
₹82.00₹22.00
The male pelvis, a crucial part of human anatomy, serves multiple functions related to structural support, locomotion, and reproductive health. The male pelvis is generally narrower and more robust than the female pelvis, reflecting differences that accommodate various biological functions. Anatomically, the male pelvis is divided into several key areas, with the pelvic cavity being the most significant. It is bounded superiorly by the pelvic brim and contains important organs, muscles, and connective tissues that contribute to its overall stability and function. The sacrum and coccyx form the posterior wall, while the ilium, ischium, and pubis make up the lateral and anterior walls respectively. The pelvic inlet, which separates the true pelvis from the false pelvis, is heart-shaped in males, a design that aids in bipedal locomotion. This configuration allows for efficient weight transfer from the upper body to the lower limbs during movement. The depth of the male pelvis further enables adequate support for internal structures while providing space for the abdominal organs above. In terms of reproductive anatomy, the male pelvis houses the reproductive organs, including the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and a portion of the vas deferens. Each of these organs plays a vital role in male fertility and sexual function. The prostate, for instance, produces a significant portion of seminal fluid, essential for sperm motility and overall reproductive health. Muscles of the pelvic floor also play a critical role in supporting pelvic organs, maintaining urinary and fecal continence, and facilitating sexual function. These muscles, often referred to as the pelvic diaphragm, include the levator ani and coccygeus. Their integrity is vital for preventing pelvic floor disorders, which can adversely affect quality of life. Understanding the male pelvis is not only essential for diagnosing ailments related to male reproductive health but also provides insights into conditions such as pelvic pain, hernias, and musculoskeletal disorders. A thorough knowledge of this anatomical region can enhance treatment strategies and improve outcomes in urology and other medical fields. In summary, the male pelvis is a complex structure that serves as a foundation for essential functions in movement, reproduction, and structural support. Its robust design and unique anatomical features reflect its critical role in the overall health and well-being of males.
Features: This median section model shows the normal position of male genital organs with bladder and rectum in the male pelvis.
Training
Providing essential healthcare training and simulation solutions.
COntacts
Support
info@medisureinternational.com
Address : 292, 7th main road Vyalikaval HBCS layout , Bangalore - 560045
+91 9972123423
© Medisure. All Rights Are Reserved
Crafted by Influence Kashmir
