رَبِّ زِدْنِي عِلْماً
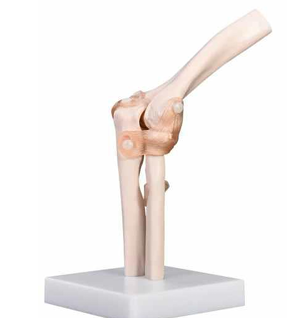
Functional Elbow Joint
Bone And Joint
₹82.00₹22.00
The elbow joint is a complex structure that plays a vital role in upper limb mobility, facilitating a range of motions crucial for daily activities. Comprised of three primary bones - the humerus, the radius, and the ulna - the elbow functions as a hinge joint, allowing flexion and extension while also enabling a degree of rotation. Anatomically, the elbow is categorized into three main articulations: the humeroulnar joint, the humeroradial joint, and the proximal radioulnar joint. 1. **Humeroulnar Joint**: This is the main joint of the elbow, where the trochlea of the humerus fits into the trochlear notch of the ulna, allowing for the bending (flexion) and straightening (extension) of the arm. 2. **Humeroradial Joint**: Located between the humerus and the radius, this joint allows for the movement of the forearm and contributes to weight-bearing activities. 3. **Proximal Radioulnar Joint**: This joint permits the rotation of the radius around the ulna, making it crucial for movements such as pronation and supination – turning the palm up or down. ### Functional Importance of the Elbow Joint The functionality of the elbow joint extends beyond simple mechanics; it is pivotal for numerous daily tasks. Here are some key aspects: - **Flexion and Extension**: The ability to bend and straighten the arm is essential for various activities, such as lifting, reaching, and throwing. The range of motion for a healthy elbow is typically between 0 degrees (fully extended) and about 150 degrees (fully flexed). - **Rotation**: The rotational capacity provided by the proximal radioulnar joint is indispensable for actions like using a screwdriver or turning a doorknob. This rotation allows the forearm to turn the palm face-up or face-down, essential for grasping and manipulating objects. - **Stability**: Ligaments surrounding the elbow joint, such as the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) and the radial collateral ligament (RCL), provide stability to the joint, especially during high-impact activities. This stability is crucial for athletes and individuals involved in activities requiring repetitive arm motions. - **Coordination with Shoulder and Wrist**: The elbow does not function in isolation; it works in concert with the shoulder and wrist joints to ensure coordinated arm movements. During many activities, the elbow acts as a link between these joints, facilitating complex motions that require precision. ### Common Injuries and Conditions Despite its robustness, the elbow joint is susceptible to various injuries and conditions that can impair its functionality. Some common issues include: - **Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)**: This condition arises from the overuse of the forearm muscles, leading to pain on the outer part of the elbow. It is prevalent among athletes and individuals engaging in repetitive wrist motions. - **Golfer's Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)**: Similar to tennis elbow, golfer's elbow affects the inner side of the elbow due to overuse, often resulting in pain and tenderness. - **Ligament Injuries**: Damage to the ligaments, particularly the UCL, can occur in sports involving overhead motions, leading to instability and pain in the elbow. - **Fractures**: Elbow fractures are common, especially in children and older adults. These can occur due to falls or direct impacts, affecting arm mobility significantly. ### Rehabilitation and Strengthening Effective rehabilitation is essential for restoring the function of the elbow joint after injury or surgery. A comprehensive program typically includes: - **Physical Therapy**: Tailored exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion are vital for recovery. Stretching and strengthening exercises target specific muscle groups to enhance joint stability and functionality. - **Gradual Return to Activities**: It is important to gradually reintroduce activities that stress the elbow joint, ensuring that the injured area adapts to increased demands without re-injury. - **Use of Braces or Supports**: In cases of ligament injuries or post-surgical recovery, braces or splints may be employed to provide additional support and stability during the healing process. ### Conclusion The elbow joint is an integral component of the upper limb, enabling a wide variety of functional movements essential for daily living and athletic performance. Understanding its anatomy, functionality, common injuries, and rehabilitation processes can aid individuals in maintaining joint health and optimizing performance. As with any joint, taking preventive measures, listening to one’s body, and seeking medical attention when needed are key aspects of safeguarding elbow functionality throughout life.
Training
Providing essential healthcare training and simulation solutions.
COntacts
Support
info@medisureinternational.com
Address : 292, 7th main road Vyalikaval HBCS layout , Bangalore - 560045
+91 9972123423
© Medisure. All Rights Are Reserved
Crafted by Influence Kashmir
